What Important Event In Animal Evolution Marks The Beginning Of The Cambrian Period? Answers.com
Introduction to Animal Diversity
The Evolutionary History of the Animal Kingdom
OpenStaxCollege
[latexpage]
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the features that characterized the earliest animals and when they appeared on earth
- Explain the significance of the Cambrian period for animal evolution and the changes in animal diversity that took place during that time
- Describe some of the unresolved questions surrounding the Cambrian explosion
- Discuss the implications of mass brute extinctions that have occurred in evolutionary history
Many questions regarding the origins and evolutionary history of the animal kingdom proceed to be researched and debated, every bit new fossil and molecular evidence change prevailing theories. Some of these questions include the following: How long accept animals existed on World? What were the earliest members of the brute kingdom, and what organism was their mutual ancestor? While animal diversity increased during the Cambrian period of the Paleozoic era, 530 one thousand thousand years ago, modern fossil evidence suggests that primitive animal species existed much before.
Pre-Cambrian Animal Life
The time earlier the Cambrian period is known as the Ediacaran period (from about 635 million years agone to 543 million years ago), the final catamenia of the late Proterozoic Neoproterozoic Era ([link]). It is believed that early on creature life, termed Ediacaran biota, evolved from protists at this time. Some protist species chosen choanoflagellates closely resemble the choanocyte cells in the simplest animals, sponges. In addition to their morphological similarity, molecular analyses accept revealed similar sequence homologies in their DNA.
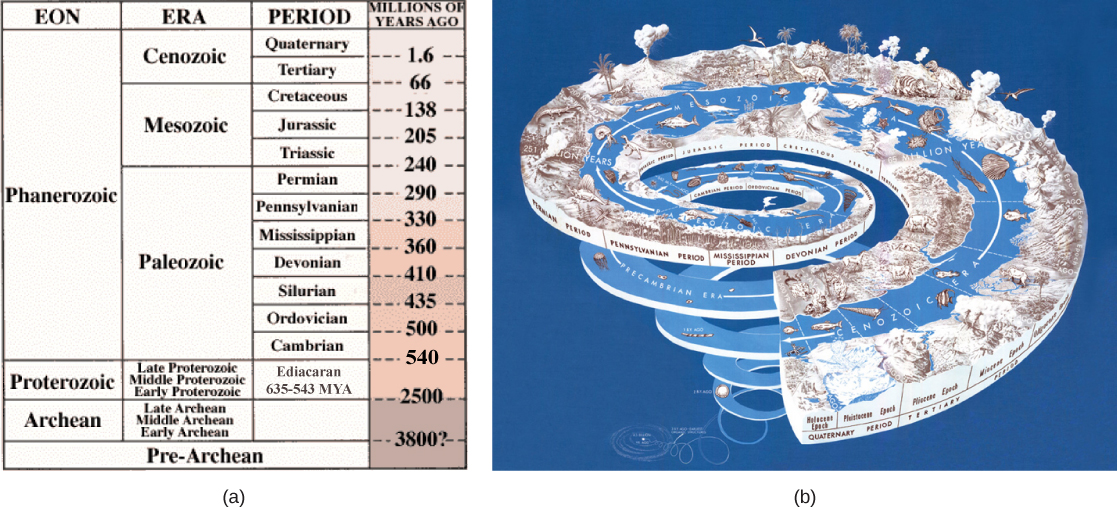
(a) Globe's history is divided into eons, eras, and periods. Note that the Ediacaran menstruum starts in the Proterozoic eon and ends in the Cambrian period of the Phanerozoic eon. (b) Stages on the geological fourth dimension scale are represented equally a spiral. (credit: modification of work by USGS)
The earliest life comprising Ediacaran biota was long believed to include only tiny, sessile, soft-bodied ocean creatures. Nonetheless, recently at that place has been increasing scientific evidence suggesting that more varied and complex animal species lived during this time, and possibly fifty-fifty before the Ediacaran period.
Fossils believed to stand for the oldest animals with hard body parts were recently discovered in South Australia. These sponge-like fossils, named Coronacollina acula, date back as far as 560 million years, and are believed to show the existence of difficult body parts and spicules that extended twenty–xl cm from the master body (estimated about 5 cm long). Other fossils from the Ediacaran period are shown in [link]ab.
Fossils of (a) Cyclomedusa and (b) Dickinsonia date to 650 one thousand thousand years ago, during the Ediacaran period. (credit: modification of work by "Smith609"/Wikimedia Commons)

Some other recent fossil discovery may stand for the earliest creature species ever found. While the validity of this merits is even so under investigation, these archaic fossils appear to be small, one-centimeter long, sponge-like creatures. These fossils from S Australia date back 650 million years, actually placing the putative animal before the great ice age extinction event that marked the transition betwixt the Cryogenian period and the Ediacaran period. Until this discovery, virtually scientists believed that there was no animal life prior to the Ediacaran period. Many scientists now believe that animals may in fact have evolved during the Cryogenian flow.
The Cambrian Explosion of Animal Life
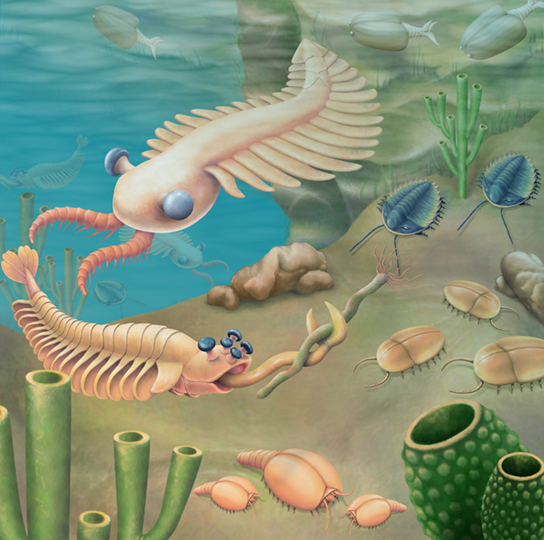
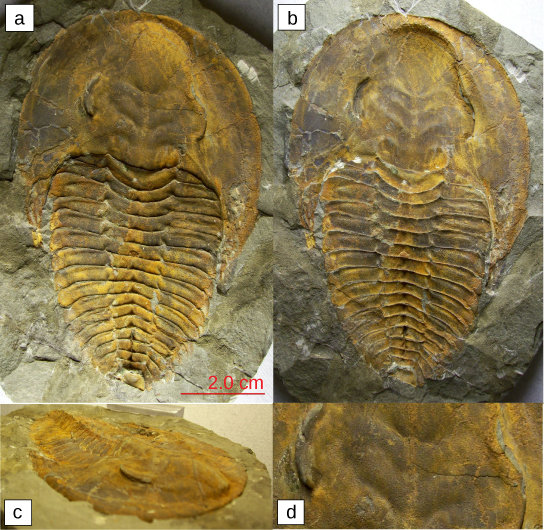
The Cambrian period, occurring between approximately 542–488 million years ago, marks the most rapid development of new creature phyla and animate being diversity in Earth's history. It is believed that about of the fauna phyla in existence today had their origins during this fourth dimension, oft referred to equally the Cambrian explosion ([link]). Echinoderms, mollusks, worms, arthropods, and chordates arose during this period. 1 of the most dominant species during the Cambrian catamenia was the trilobite, an arthropod that was among the first animals to exhibit a sense of vision ([link]abcd).
An artist'southward rendition depicts some organisms from the Cambrian period.

These fossils (a–d) belong to trilobites, extinct arthropods that appeared in the early Cambrian period, 525 million years ago, and disappeared from the fossil record during a mass extinction at the end of the Permian menstruation, virtually 250 million years ago.
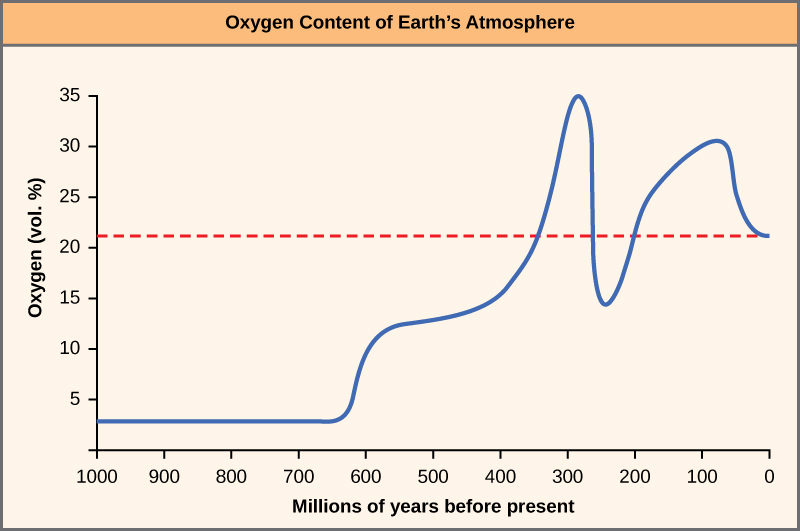
The cause of the Cambrian explosion is still debated. There are many theories that effort to reply this question. Environmental changes may have created a more suitable surroundings for creature life. Examples of these changes include rising atmospheric oxygen levels and big increases in oceanic calcium concentrations that preceded the Cambrian flow ([link]). Some scientists believe that an expansive, continental shelf with numerous shallow lagoons or pools provided the necessary living infinite for larger numbers of unlike types of animals to co-exist. There is also support for theories that contend that ecological relationships betwixt species, such as changes in the food web, competition for nutrient and infinite, and predator-casualty relationships, were primed to promote a sudden massive coevolution of species. Withal other theories claim genetic and developmental reasons for the Cambrian explosion. The morphological flexibility and complexity of animal evolution afforded by the evolution of Hox control genes may have provided the necessary opportunities for increases in possible animate being morphologies at the time of the Cambrian period. Theories that endeavor to explain why the Cambrian explosion happened must exist able to provide valid reasons for the massive animal diversification, also every bit explain why it happened when it did. At that place is show that both supports and refutes each of the theories described higher up, and the answer may very well exist a combination of these and other theories.
The oxygen concentration in Earth'southward atmosphere rose sharply effectually 300 one thousand thousand years agone.
However, unresolved questions nigh the animal diversification that took place during the Cambrian period remain. For case, we practise not understand how the evolution of so many species occurred in such a short flow of fourth dimension. Was at that place really an "explosion" of life at this detail time? Some scientists question the validity of the this idea, because there is increasing evidence to suggest that more beast life existed prior to the Cambrian menstruum and that other similar species' so-chosen explosions (or radiations) occurred later in history also. Furthermore, the vast diversification of animal species that appears to have begun during the Cambrian menstruum continued well into the following Ordovician period. Despite some of these arguments, nearly scientists agree that the Cambrian period marked a time of impressively rapid animal development and diversification that is unmatched elsewhere during history.
Post-Cambrian Evolution and Mass Extinctions
The periods that followed the Cambrian during the Paleozoic Era are marked past farther animal evolution and the emergence of many new orders, families, and species. As brute phyla continued to diversify, new species adjusted to new ecological niches. During the Ordovician period, which followed the Cambrian flow, plant life first appeared on land. This change allowed formerly aquatic creature species to invade land, feeding straight on plants or decomposable vegetation. Continual changes in temperature and moisture throughout the remainder of the Paleozoic Era due to continental plate movements encouraged the development of new adaptations to terrestrial beingness in animals, such as limbed appendages in amphibians and epidermal scales in reptiles.
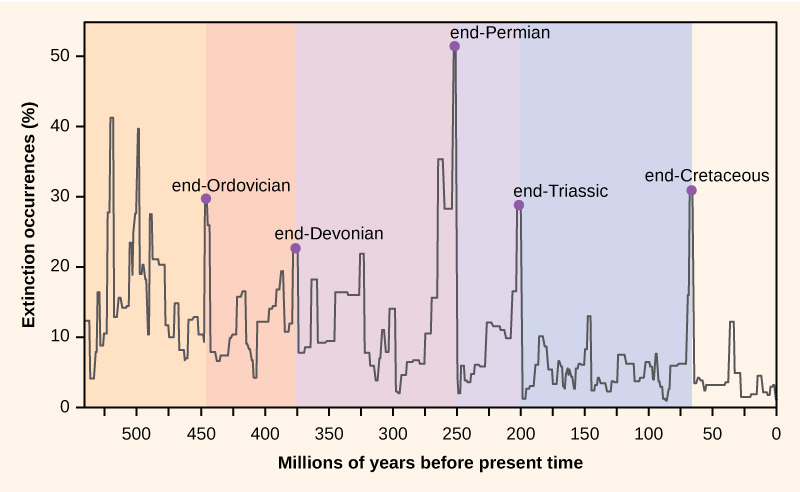
Changes in the surroundings often create new niches (living spaces) that contribute to rapid speciation and increased multifariousness. On the other hand, cataclysmic events, such as volcanic eruptions and meteor strikes that obliterate life, can result in devastating losses of diversity. Such periods of mass extinction ([link]) take occurred repeatedly in the evolutionary record of life, erasing some genetic lines while creating room for others to evolve into the empty niches left behind. The end of the Permian period (and the Paleozoic Era) was marked past the largest mass extinction effect in Globe's history, a loss of roughly 95 per centum of the extant species at that time. Some of the dominant phyla in the world's oceans, such equally the trilobites, disappeared completely. On land, the disappearance of some dominant species of Permian reptiles fabricated it possible for a new line of reptiles to sally, the dinosaurs. The warm and stable climatic conditions of the ensuing Mesozoic Era promoted an explosive diversification of dinosaurs into every conceivable niche in country, air, and water. Plants, too, radiated into new landscapes and empty niches, creating complex communities of producers and consumers, some of which became very big on the arable nutrient available.
Another mass extinction event occurred at the end of the Cretaceous period, bringing the Mesozoic Era to an end. Skies darkened and temperatures savage equally a large meteor impact and tons of volcanic ash blocked incoming sunlight. Plants died, herbivores and carnivores starved, and the mostly cold-blooded dinosaurs ceded their dominance of the landscape to more warm-blooded mammals. In the post-obit Cenozoic Era, mammals radiated into terrestrial and aquatic niches once occupied by dinosaurs, and birds, the warm-blooded offshoots of one line of the ruling reptiles, became aerial specialists. The advent and authority of flowering plants in the Cenozoic Era created new niches for insects, as well equally for birds and mammals. Changes in creature species variety during the late Cretaceous and early Cenozoic were likewise promoted by a dramatic shift in Earth's geography, equally continental plates slid over the crust into their current positions, leaving some fauna groups isolated on islands and continents, or separated past mount ranges or inland seas from other competitors. Early in the Cenozoic, new ecosystems appeared, with the development of grasses and coral reefs. Belatedly in the Cenozoic, further extinctions followed past speciation occurred during ice ages that covered high latitudes with ice and and then retreated, leaving new open spaces for colonization.
Link to Learning

Watch the following video to larn more than about the mass extinctions.
Mass extinctions accept occurred repeatedly over geological time.
Career Connexion
PaleontologistNatural history museums incorporate the fossil casts of extinct animals and information about how these animals evolved, lived, and died. Paleontogists are scientists who study prehistoric life. They utilize fossils to find and explain how life evolved on Globe and how species interacted with each other and with the environment. A paleontologist needs to exist knowledgeable in biology, ecology, chemistry, geology, and many other scientific disciplines. A paleontologist's work may involve field studies: searching for and studying fossils. In add-on to digging for and finding fossils, paleontologists also ready fossils for further written report and analysis. Although dinosaurs are probably the outset animals that come to mind when thinking well-nigh paleontology, paleontologists report everything from plant life, fungi, and fish to sea animals and birds.
An undergraduate degree in earth science or biology is a good place to start toward the career path of becoming a paleontologist. Most often, a graduate degree is necessary. Additionally, piece of work feel in a museum or in a paleontology lab is useful.
Section Summary
The most rapid diversification and evolution of animal species in all of history occurred during the Cambrian period of the Paleozoic Era, a miracle known every bit the Cambrian explosion. Until recently, scientists believed that in that location were only very few tiny and simplistic creature species in existence before this flow. Withal, recent fossil discoveries have revealed that additional, larger, and more than complex animals existed during the Ediacaran menses, and even possibly earlier, during the Cryogenian menstruum. Still, the Cambrian period undoubtedly witnessed the emergence of the majority of animal phyla that nosotros know today, although many questions remain unresolved nearly this historical phenomenon.
The residuum of the Paleozoic Era is marked past the growing appearance of new classes, families, and species, and the early colonization of land by certain marine animals. The evolutionary history of animals is also marked past numerous major extinction events, each of which wiped out a bulk of extant species. Some species of near animate being phyla survived these extinctions, assuasive the phyla to persist and keep to evolve into species that nosotros meet today.
Review Questions
Which of the following periods is the earliest during which animals may have appeared?
- Ordovician flow
- Cambrian menstruation
- Ediacaran period
- Cryogenian period
D
What blazon of information is primarily used to decide the existence and advent of early animal species?
- molecular data
- fossil information
- morphological data
- embryological development data
B
The time betwixt 542–488 million years agone marks which menstruum?
- Cambrian period
- Silurian period
- Ediacaran period
- Devonian menstruum
A
Until recent discoveries suggested otherwise, animals existing before the Cambrian period were believed to exist:
- small and ocean-dwelling
- small and non-motile
- small and soft-bodied
- small and radially symmetrical or asymmetrical
C
Plant life first appeared on country during which of the following periods?
- Cambrian period
- Ordovician flow
- Silurian period
- Devonian period
B
Approximately how many mass extinction events occurred throughout the evolutionary history of animals?
- 3
- 4
- 5
- more than 5
D
Free Response
Briefly describe at least two theories that attempt to explain the cause of the Cambrian explosion.
One theory states that ecology factors led to the Cambrian explosion. For example, the rise in atmospheric oxygen and oceanic calcium levels helped to provide the right environmental conditions to permit such a rapid evolution of new animal phyla. Some other theory states that ecological factors such as competitive pressures and predator-prey relationships reached a threshold that supported the rapid animal evolution that took place during the Cambrian period.
How is it that virtually, if not all, of the extant animate being phyla today evolved during the Cambrian menses if so many massive extinction events have taken identify since then?
It is true that multiple mass extinction events take taken place since the Cambrian menses, when near currently existing beast phyla appeared, and the bulk of animal species were commonly wiped out during these events. However, a small number of beast species representing each phylum were commonly able to survive each extinction consequence, allowing the phylum to keep to evolve rather than become altogether extinct.
Glossary
- Cambrian explosion
- time during the Cambrian period (542–488 million years ago) when most of the animal phyla in existence today evolved
- Cryogenian catamenia
- geologic period (850–630 million years ago) characterized by a very common cold global climate
- Ediacaran flow
- geological period (630–542 million years ago) when the oldest definite multicellular organisms with tissues evolved
- mass extinction
- upshot that wipes out the majority of species within a relatively short geological time menstruum
Source: https://pressbooks-dev.oer.hawaii.edu/biology/chapter/the-evolutionary-history-of-the-animal-kingdom/
Posted by: thiesputed1978.blogspot.com


0 Response to "What Important Event In Animal Evolution Marks The Beginning Of The Cambrian Period? Answers.com"
Post a Comment